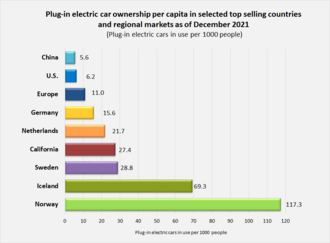
Electric vehicles (EVs) adoption varies significantly across different countries and regions. Factors include government policies, infrastructure, and consumer preferences.
Electric vehicles are transforming the global automotive landscape, but their adoption rates differ widely. Some countries, like Norway, lead the world in EV adoption due to strong government incentives and a robust charging infrastructure. China and the United States are also significant players, with large-scale investments in EV technology and infrastructure.
Meanwhile, other regions lag due to economic constraints or lack of supportive policies. Understanding these differences is crucial for stakeholders aiming to advance EV adoption worldwide. This comparative analysis will shed light on the key factors influencing EV uptake in various regions, providing insights for policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike.
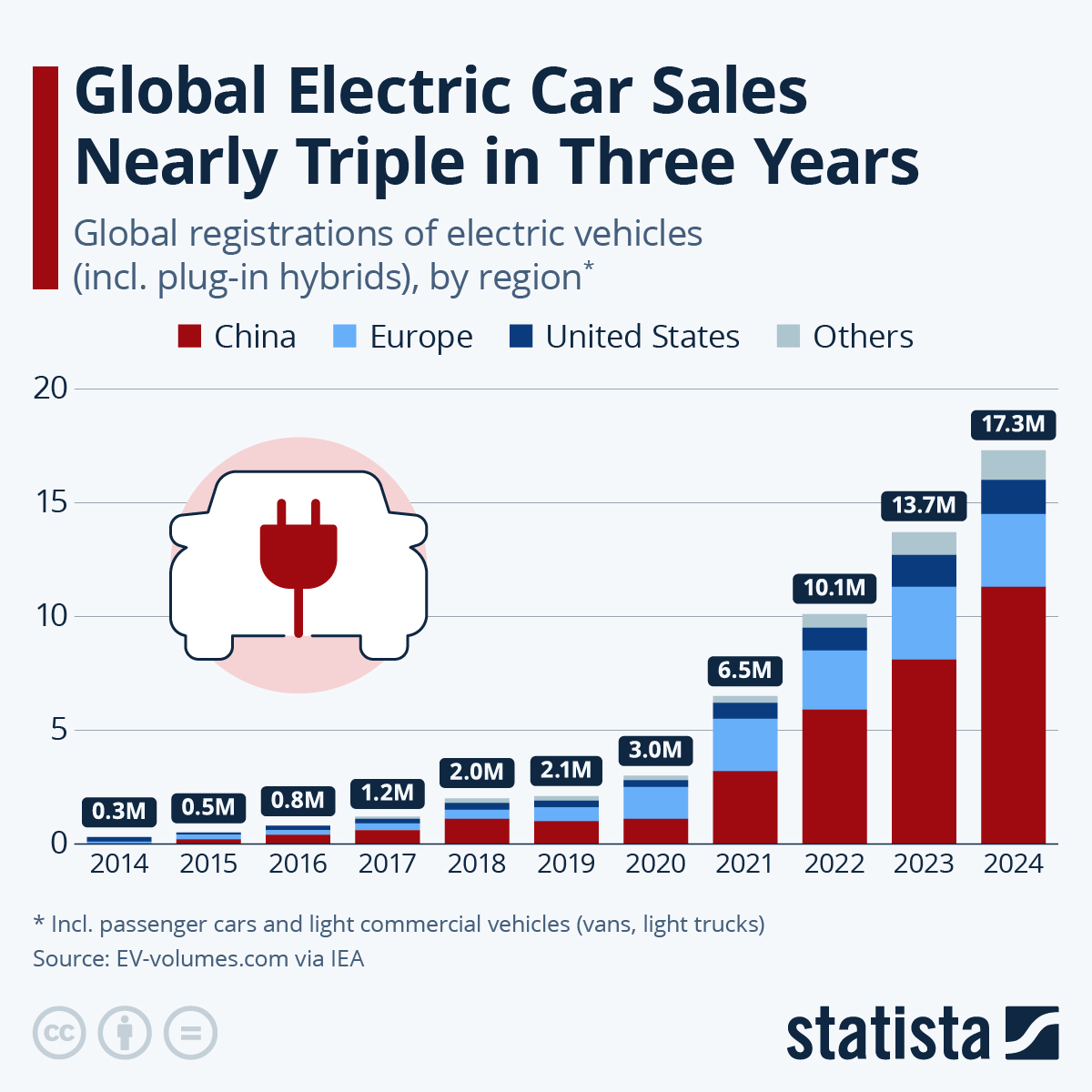
Credit: www.statista.com
Comparing EVs Across Different Countries Regions: Ev Adoption Rates
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption rates vary across different countries and regions. Understanding these differences helps us see global trends and progress in green technology. In this section, we will explore leading countries and emerging markets in EV adoption.
Leading Countries
The leading countries in EV adoption are making significant strides. These nations have high EV sales, supportive policies, and robust charging infrastructure.
| Country | EV Market Share | Charging Stations |
|---|---|---|
| Norway | 54% | 16,000 |
| Netherlands | 25% | 75,000 |
| China | 10% | 800,000 |
Norway leads with 54% EV market share, the highest globally. The Netherlands follows with 25%, and China has 10%. These countries invest heavily in EV infrastructure and incentives.
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets show promising growth in EV adoption. These regions are witnessing a surge in EV sales and infrastructure development.
- India: Rapidly expanding EV market with government support.
- Brazil: Increasing EV sales and infrastructure projects.
- South Africa: Growth in EV adoption and charging stations.
India, Brazil, and South Africa are notable emerging markets. They are focusing on policies and incentives to boost EV adoption.
These emerging markets are crucial for global EV adoption. Their growth will contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions.

Credit: www.statista.com
Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the electric vehicle (EV) market across different countries and regions. These policies can either accelerate or hinder the adoption of EVs. Here, we will examine how government interventions, such as subsidies and regulatory frameworks, affect the EV landscape globally.
Subsidies And Incentives
Governments offer various subsidies and incentives to encourage EV adoption. These financial aids make EVs more affordable for consumers. Below is a table highlighting the subsidies and incentives in different countries:
| Country/Region | Subsidies | Incentives |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Up to $7,500 tax credit | Free parking, HOV lane access |
| Germany | Up to €9,000 grant | Reduced road tax, free charging |
| China | Up to ¥20,000 subsidy | Exemption from license plate restrictions |
| India | Up to ₹150,000 subsidy | Income tax benefits, reduced GST |
These financial benefits significantly reduce the initial cost of purchasing an EV. This makes EVs more accessible to a broader audience.
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks set the rules for EV adoption and infrastructure. These rules ensure the safe and efficient use of EVs. Different regions have distinct regulatory approaches:
- USA: Strict emissions standards, federal and state level regulations
- European Union: CO2 emission targets, city-level low-emission zones
- China: New Energy Vehicle (NEV) mandate, city-specific policies
- India: Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) policy
These frameworks influence the availability of charging stations, battery recycling, and vehicle safety standards. They also determine the pace of EV adoption in each region.
Understanding these government policies helps consumers and manufacturers navigate the EV market. This knowledge can guide better decisions and investments in the EV sector.
Charging Infrastructure
The charging infrastructure is crucial for electric vehicles (EVs). It helps drivers recharge their cars easily. Different countries have different setups for EV charging. This section will explore public charging stations and home charging solutions in various regions.
Public Charging Stations
Public charging stations are essential for long trips. They are usually found in cities, highways, and parking lots. Countries like the United States and Norway have many public chargers. Some regions offer fast chargers, while others have slower options.
Here is a comparison of public charging stations:
| Country | Number of Stations | Fast Chargers |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 100,000+ | Yes |
| Norway | 15,000+ | Yes |
| India | 5,000+ | No |
Home Charging Solutions
Many EV owners prefer home charging. It is convenient and cost-effective. Different regions offer various home charging setups. In the US and Europe, people use Level 2 chargers at home. These chargers are faster than regular outlets.
Here are some benefits of home charging:
- Convenient and easy to use
- Cheaper than public charging
- Charges overnight
Some countries provide incentives for home chargers. For example, the UK offers grants for installing home charging points. This encourages more people to buy EVs.
Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences for electric vehicles (EVs) vary across countries and regions. Cultural factors, economic conditions, and government policies play significant roles. Understanding these preferences helps in identifying the popular EV models, their range, and performance in different areas.
Popular Ev Models
Different countries have different popular EV models. Below is a table highlighting some of the top choices:
| Country/Region | Popular EV Models |
|---|---|
| United States | Tesla Model 3, Ford Mustang Mach-E |
| Europe | Volkswagen ID.3, Renault Zoe |
| China | BYD Han, NIO ES6 |
| Japan | Nissan Leaf, Honda e |
Tesla Model 3 and Volkswagen ID.3 are globally recognized. BYD Han and Nissan Leaf are regional favorites.
Range And Performance
Range and performance are crucial factors for EV consumers. These preferences also vary widely:
- United States: Consumers prefer long-range EVs. Tesla Model S offers over 370 miles per charge.
- Europe: Compact EVs with moderate range are popular. Renault Zoe provides about 245 miles.
- China: Affordable EVs with decent range are in demand. BYD Han offers around 300 miles.
- Japan: Urban-friendly EVs with smaller range are favored. Honda e provides 137 miles.
Long-range and performance are key factors in the U.S. Compact and urban EVs are more popular in Europe and Japan.
Environmental Impact
Electric vehicles (EVs) play a significant role in reducing environmental harm. Different countries and regions have unique approaches to maximize these benefits.
Emission Reductions
EVs reduce harmful emissions significantly compared to traditional cars. Below is a table showing CO2 emissions per kilometer in various regions:
| Region | CO2 Emissions (g/km) |
|---|---|
| United States | 100 |
| Europe | 75 |
| China | 90 |
| India | 110 |
Europe leads with the lowest CO2 emissions per kilometer. This is due to stringent regulations and high EV adoption rates.
Renewable Energy Integration
Using renewable energy sources enhances the benefits of EVs. Countries with abundant renewable energy see greater environmental gains.
Norway sources most of its electricity from hydropower. This makes its EVs nearly emission-free. Germany is increasing solar and wind power to charge EVs sustainably.
- Norway: 98% electricity from hydropower
- Germany: 40% electricity from solar and wind
- Australia: Rapid growth in solar energy use
Countries with high renewable energy integration see more environmental benefits from EVs. Combining EVs with clean energy is key to reducing emissions further.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a crucial role in the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). These factors include cost of ownership and market trends. Understanding these can help you decide which country or region is best for EVs.
Cost Of Ownership
The cost of ownership for EVs varies across different countries. Several factors contribute to this variance:
- Initial Purchase Price: This includes taxes, subsidies, and incentives.
- Maintenance Costs: EVs generally have lower maintenance costs.
- Fuel Costs: Electricity prices differ from one region to another.
Below is a comparison table for the cost of ownership in three different countries:
| Country | Initial Purchase Price | Annual Maintenance Cost | Annual Fuel Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | $30,000 | $500 | $400 |
| Germany | €28,000 | €450 | €350 |
| China | ¥200,000 | ¥2,500 | ¥2,000 |
Market Trends
Market trends influence the availability and popularity of EVs in different regions. Key trends include:
- Government Policies: Incentives and regulations impact EV adoption.
- Consumer Preferences: More people prefer eco-friendly vehicles.
- Charging Infrastructure: Availability of charging stations is crucial.
Here are some current market trends:
- In the USA, government incentives boost EV sales.
- Germany focuses on expanding charging infrastructure.
- China leads in EV production and sales.
Technological Advancements
The world of Electric Vehicles (EVs) is evolving rapidly across different countries and regions. Technological advancements are at the heart of these transformations. This section delves into the significant developments in Battery Technology and Autonomous Driving.
Battery Technology
Battery technology is crucial for the success of EVs. Various countries are pioneering advancements in this field.
- United States: The U.S. focuses on developing solid-state batteries. These batteries promise higher energy density and faster charging times.
- China: China leads in Lithium-Iron-Phosphate (LFP) batteries. LFP batteries are cost-effective and have a longer lifespan.
- Europe: European countries invest in next-gen lithium-ion batteries. These batteries aim to improve energy storage and reduce costs.
Here’s a table comparing the battery technologies:
| Country/Region | Battery Type | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Solid-State | Higher energy density, Faster charging |
| China | Lithium-Iron-Phosphate | Cost-effective, Longer lifespan |
| Europe | Next-Gen Lithium-Ion | Improved energy storage, Reduced costs |
Autonomous Driving
Autonomous driving technology is revolutionizing the EV market. Different regions are making strides in this area.
- United States: The U.S. leads in autonomous driving research. Companies like Tesla and Waymo are at the forefront.
- China: China is rapidly catching up. Baidu’s Apollo project is a major player in autonomous driving.
- Europe: Europe focuses on safety and regulations. Countries like Germany are setting high standards for autonomous vehicles.
Autonomous driving technologies vary significantly:
| Country/Region | Key Players | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Tesla, Waymo | Research and Development |
| China | Baidu Apollo | Rapid Implementation |
| Europe | Various Automakers | Safety and Regulation |
Technological advancements in EVs are shaping the future of transportation globally. Battery technology and autonomous driving are two key areas leading this change.
Challenges And Barriers
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining traction globally. Yet, challenges and barriers vary across countries and regions. These obstacles impact the adoption rate and consumer confidence. This section explores key hurdles in different areas.
Infrastructure Gaps
Charging infrastructure is crucial for EV adoption. Some regions have widespread charging networks. Others lag behind, creating challenges for EV owners.
- Urban vs. Rural: Cities often have more charging stations. Rural areas face shortages.
- Public vs. Private: Public charging spots are limited. Home charging is not always possible.
Countries like Norway lead with ample chargers. In contrast, developing nations struggle with limited infrastructure.
Consumer Skepticism
Many consumers remain skeptical about EVs. This skepticism stems from various factors. Understanding these can help address concerns.
- Range Anxiety: Fear of running out of charge worries many. Improved battery tech can alleviate this.
- Cost Concerns: EVs often have higher upfront costs. Incentives and subsidies can help.
- Maintenance Myths: Some think EVs are hard to maintain. In reality, they require less maintenance than ICE vehicles.
Educating consumers is essential. Clear information can turn skepticism into confidence.
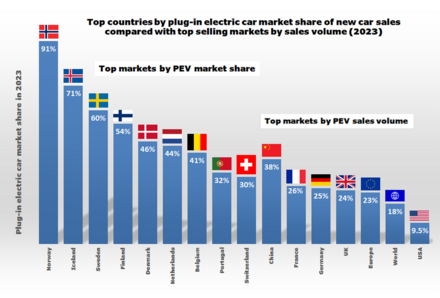
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Country Has The Most Evs?
China has the most electric vehicles (EVs). The country leads globally in EV adoption and sales, surpassing other nations.
Which Country Has The Best Ev Policy?
Norway leads with the best EV policy. They offer significant incentives, including tax exemptions and free parking. Their policies promote rapid electric vehicle adoption.
Why Are Ev Sales So High In Norway?
EV sales are high in Norway due to strong government incentives, extensive charging infrastructure, and high environmental awareness among citizens.
Which Us State Has The Most Evs?
California has the most electric vehicles in the US. The state leads due to its strong EV incentives and infrastructure.
Conclusion
Exploring EV adoption across countries reveals unique trends. Each region faces distinct challenges and opportunities. Governments play a crucial role. Incentives and infrastructure development are key. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate global progress. Embrace the electric future, wherever you are.