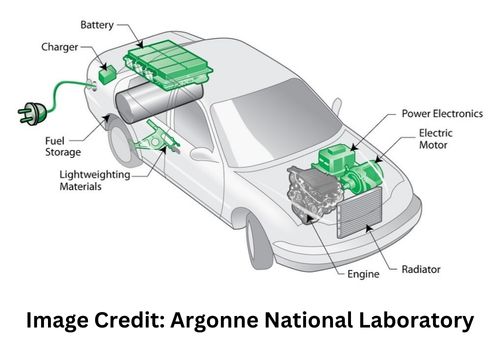
The most expensive, vital, and, most crucially, disputed part of an electric car is the battery. EV Batteries are frequently cited as the main issue by those who oppose electric vehicles, who point out their short lifespan, requirement for early replacement, and environmental impact of recycling. Numerous of the assertions were once true, but they are now false.
Manufacturers of EV batteries for electric vehicles are numerous. Nissan and Tesla are two prominent examples. For instance, LG Chem offers batteries for electric vehicles to Volvo, Renault, Ford, and Chevrolet. Additionally, they signed a contract with Tesla under which they will provide batteries for each Tesla made in China.
Leading producer of electric vehicles in China, BYD is also developing battery-based electricity storage systems for residential, commercial, and industrial use. Hybrid electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, and battery electric vehicles are the three categories under which electric vehicle technology is divided.
Recycling electric vehicle (EV) batteries is important in order to properly dispose of used batteries and reduce the environmental impact of EVs. Here are five methods of recycling EV batteries that you should know about:
- Dismantling: This method involves breaking down the battery into its component parts, such as the cathode, anode, and separator, which can be recycled separately.
- Thermal treatment: This method involves heating the battery to high temperatures in order to melt down the metal components, which can then be separated and recycled.
- Chemical treatment: This method involves using chemicals to break down the battery into its component parts, which can then be recycled.
- Physical treatment: This method involves shredding or crushing the battery in order to separate the metal components, which can then be recycled.
- Reuse: Some EV batteries can be refurbished and reused in other applications, such as energy storage systems or as backup power for homes and businesses.
Overall, recycling EV batteries is an important aspect of the lifecycle of EVs, and there are several methods that can be used to properly dispose of used batteries and reduce the environmental impact of EVs.
Does Electric Batteries Are Recyclable?
Only 5% of batteries for electric vehicles were recycled in 2019, and battery manufacturers do not currently consider recycling when designing new batteries.
There are five types of recycling methods currently available:
- Pyrometallurgical recovery,
- Physical materials separation,
- Hydrometallurgical metal reclamation,
- Direct recycling method, and
- Biological metals reclamation.
The first three methods mentioned are the ones that are used the most frequently. The last two strategies are still in the lab or are being tested on a small scale, but they offer the most potential to reduce mining emissions. With the intention of recycling 97% of battery components, VW has announced the opening of a pilot battery recycling facility. During this procedure, batteries will be shredded, dried, and sieved to extract valuable elements that can be used to make new batteries.
How Does EV Batteries Works ?

In contrast to electric vehicles, which are propelled by electromagnetic radiation, internal combustion technology powers a vehicle by fusing combustion and pressure. The regenerative braking system of electric vehicles then absorbs the electric energy and stores it in batteries, minimizing energy waste and pollution. An electric vehicle obtains its power straight from a sizable battery pack, as opposed to internal combustion-engine cars, which get their energy from burning gasoline or fuel.
These resemble a bigger version of the lithium-ion battery in your smartphone since electric vehicles (EVs) employ packs of thousands of Li-ion cells rather than a single battery like a phone. While the car is charging, electricity is used to cause chemical reactions inside the batteries. These modifications are then reversed while it is moving to produce power.
ALSO READ THIS : How Does Electric Vehicles Save Environment
How EV Batteries Are Made ?

In contrast to starter, lighting, and ignition batteries, deep-cycle batteries used in electric car batteries are designed to supply power for lengthy periods of time.
Smaller, lighter batteries are favored because they reduce vehicle weight and hence improve performance. Electric car batteries are distinguished by their relatively high power-to-weight ratio, specific energy, and energy density. When compared to liquid fuels, the majority of modern battery technologies have significantly lower specific energies, which commonly affects the vehicles’ maximum all-electric range.
The most common battery types in contemporary electric vehicles are lithium-ion and lithium polymer batteries because of their high energy density relative to weight. Batteries for electric vehicles can also be made of lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride, zinc-air, and, less frequently, sodium nickel chloride.
How these Batteries are used in Electric Car ?
Deep cycle batteries are used to continuously power electric vehicles like forklifts and golf carts, whereas automobile engine starting batteries are designed to utilize a tiny portion of their capacity to deliver high charge rates to start the engine.
Due to their well-established technology, wide availability, and affordable price, lead-acid batteries were previously utilized in the majority of electric vehicles, such as the Detroit Electric Vehicles and General Motors EV1.
The usage of nickel-metal hydride batteries in hybrid cars and the first-generation NiMH Toyota RAV4 EVs that are still operating after 100,000 miles and more than ten years of use demonstrate that nickel-metal hydride batteries can have an extremely long lifespan when utilized properly.
A sodium nickel chloride, or “Zebra” battery, serves as the electrolyte. Many different EVs, like the Modec commercial vehicle, have used them. Zebra batteries can withstand countless charge cycles and are safe to use. Since the late 1990s, demands from portable electronics, laptop computers, mobile phones, and power tools have driven advancements in lithium-ion battery technology.
The performance and energy density improvements have helped the BEV and HEV markets. Lithium-ion batteries, in contrast to earlier battery chemistries like nickel-cadmium, can be discharged and recharged frequently and at any charge level. Lithium is also the lightest metal.
However, lithium-ion batteries only contain ions and not lithium metal. An atom or molecule that has an electric charge as a result of losing or gaining one or more electrons is known as an ion. In addition to being safer than many alternatives, lithium-ion batteries also come with a number of safety measures that battery makers are obligated to put in place to protect consumers in the unusual case of a battery failure.
Electric vehicle manufacturers, for instance, incorporate charging protections to protect the batteries during frequent, quick charges that take place quickly. When an electric vehicle is plugged in, the battery undergoes cycles of “discharge” while driving and “charge.” Repeating this process causes the battery’s capacity to hold charge to decline over time.
As a result, it takes less time and has a longer range. The majority of battery producers offer a five to eight-year warranty. A battery for an electric vehicle is expected to last between 10 and 20 years before needing to be replaced.
Surprisingly, the connection between a battery and an electric motor in a car is straightforward and obvious :
The wheels are moved by the batteries through a connection to one or more electric motors. Pushing the accelerator immediately powers the motor, which then gradually consumes the energy in the batteries. When you take your foot off the accelerator, the automobile starts to slow down by converting its forward momentum back into power since electric motors may also act as generators.
If you apply the brakes, this effect is amplified. By recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted during braking, regenerative braking increases the vehicle’s range by storing the energy in the battery.
By adding to a battery storage system, an EV battery that can no longer power a car can still be used to power a house or other structure. An energy storage system with batteries stores energy to be used later. You can combine an EV battery with renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
You can keep it and utilize it at night when the wind and sunlight are lessened. Additionally, you can use wind or solar energy during the day. You can reduce your reliance on the grid and lower your utility costs by using this method of energy production.
The battery in an electric vehicle is a tried-and-true technology that will endure for a long time. Even EV manufacturers promise it. For instance, Nissan promises that the batteries in its electric vehicles would last eight years or 100,000 miles, and Tesla makes a comparable promise. This may seem unbelievable when the battery in your phone starts to fail after only a few years, but during that time, it may have gone through hundreds of full charges and discharges.
ALSO READ THIS : Pros And Cons Of Electric Car
Charging other Electronic devices decrease the battery’s life ?
A lithium-ion phone battery starts to lose a significant amount of its capacity after 500 complete cycles. While it could be adequate for a phone, it is insufficient for a vehicle designed to travel thousands of miles, hence EV manufacturers make great efforts to increase the battery life of electric vehicles.
Because EV batteries are buffered, drivers cannot use the complete amount of power that is stored, reducing the number of cycles the battery undergoes. This suggests that the batteries in electric cars should live for many years when combined with additional methods like intelligent cooling systems. In reality, to increase the lifespan of an electric vehicle battery, manufacturers make sure there is sufficient spare capacity to account for depreciation over time.
The excess spare capacity is used up as electric cars get older and their batteries go through more cycles. As a result, the vehicle’s range can be maintained over the battery’s lifespan. Drivers may notice a drop in battery performance and range when the battery capacity falls below 80%.
As battery technology advances and production volumes rise, plug-in electric vehicles will become more competitive with conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. Because many manufacturers offer warranties of up to 8 years or 100,000 miles, you don’t have to worry about changing an electric vehicle’s battery.
It might be covered by this guarantee even if you had to replace it in the unfortunate event that something went wrong. Always verify the sort of warranty offered by the manufacturer of your preferred electric vehicle. EV batteries eventually need to be thrown away, even though enabling a second-life application can prolong their life.
Do Electric Car Batteries harm the Environment?
Here to let you know that things are looking up for EV batteries in the future. EV batteries can be recycled into the energy cycle to power factories and homes once their life as car batteries is ended. A closed-loop recycling system might be created by recycling EV batteries. In other words, once the batteries’ time as automotive power sources is up, the factories that create the batteries might eventually be powered by the recycled batteries.
Large automobile manufacturers have already started reusing EV batteries in a variety of uses. It might be challenging to get rid of batteries of all kinds without harming the environment. With EV batteries, the same is true.
EV battery life cycle management, on the other hand, aims to address the issue of pricy and hazardous battery disposal. In addition to being used to support the use
of renewable energy, EV batteries can be repaired to help power more vehicles in the future.
The Volkswagen Group plans to introduce a recycling program in which batteries will be classified according to quality to determine their ultimate destination. The batteries that are still functional will serve as mobile automobile charging power packs. The international standard covers many of the safety issues with battery electric vehicles.
Firefighters and rescue personnel receive specialized training to deal with the higher voltages and toxins present in incidents involving electric and hybrid vehicles. Many experts concur that BEV batteries are safe in commercially available vehicles and rear-end collisions and that they are safer than gasoline-powered cars with rear gas tanks, despite the fact that BEV accidents may present unexpected challenges, such as fires and smells caused by rapid battery discharge.
