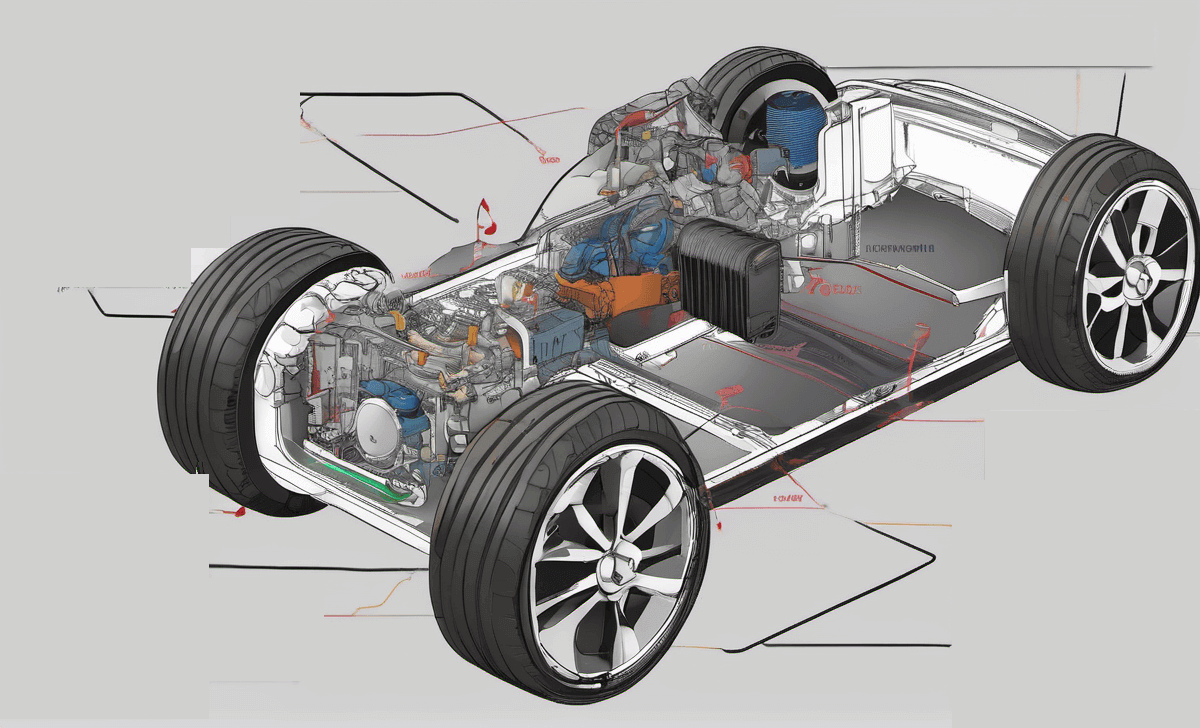
Components of Powertrain of Electric Car
The powertrain of an electric car comprises various components that work in harmony to convert electrical energy into mechanical power for propulsion. Understanding the intricacies of these components of powertrain is essential to grasp the functioning of an electric vehicle.
The powertrain of an electric vehicle (EV) is made up of several components such as Battery pack, Inverters, Electric motor, Transmission, DC converter, Auxiliary battery.
The powertrain also includes three main energy conversion systems:
- Traction inverter
- On-board charging system
- DC-to-DC converter
Additional components in the powertrain of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles include: ICE, Dedicated transmission, Exhaust system.
The powertrain is the assembly of all the components that move a vehicle forward. It generates power from the engine and delivers it to the wheels.
Let’s delve into the details of the key components that make up an electric car powertrain:
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Pack | Stores electrical energy | Powers the electric motor |
| Electric Motor | Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy | Propels the wheels of the car |
| Controller Unit | Manages the flow of electricity from the battery pack to the motor and regulates the motor’s speed and torque | Controls the powertrain and optimizes performance |
| Inverter | Converts the direct current (DC) electricity from the battery pack into alternating current (AC) electricity | Supplies AC electricity to the electric motor |
| Charger | Replenishes the electrical energy in the battery pack | Converts AC electricity from the grid into DC electricity for charging |
| Transmission (In some electric cars) | Transfers mechanical power from the electric motor to the wheels | Enhances efficiency and performance |
| Thermal Management System | Maintains proper operating temperatures for the battery pack, electric motor, and other components | Ensures optimal performance and longevity of the powertrain |
| Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) | Manages and coordinates various systems, including the electric motor, battery, charging, and regenerative braking | Serves as the “brain” of the powertrain and manages its overall operation |
| Regenerative Braking System | Harnesses kinetic energy during braking or deceleration | Converts kinetic energy into electrical energy for storage in the battery and improves efficiency |
1. Electric Motor
The electric motor serves as the heart of the electric car powertrain. It is the main source of propulsion, transforming electrical energy into mechanical power. The motor employs electromagnetic principles to generate rotational motion, propelling the vehicle forward with remarkable efficiency and torque.
2. Battery Pack
The battery pack acts as the energy reservoir for an electric car. Composed of numerous lithium-ion cells, it stores electrical energy that powers the electric motor. The battery pack’s capacity and energy density directly impact the range and performance of the electric vehicle, enabling it to travel substantial distances on a single charge.
3. Power Inverter
The power inverter is a critical component that converts the direct current (DC) supplied by the battery pack into alternating current (AC) suitable for the electric motor’s operation. It ensures efficient power delivery and control, allowing the motor to operate optimally at varying speeds and torque levels.
4. Battery Management System (BMS)
The battery management system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the battery pack’s performance. It regulates the charging and discharging processes, ensures balanced cell voltages, and safeguards against overcharging or overheating. The BMS optimizes battery lifespan, performance, and safety, enhancing overall powertrain efficiency.
5. Motor Controller
The motor controller is an electronic device that governs the operation of the electric motor. It manages the power flow, adjusts the motor’s speed and torque output, and coordinates with other powertrain components. The motor controller plays a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency, responsiveness, and smoothness of the electric car’s drive.
6. Transmission
In electric vehicles, the transmission system is simpler compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Many electric cars employ a single-speed transmission or direct drive system, which eliminates the need for complex gear shifting. This streamlined transmission design contributes to the overall efficiency and simplicity of the electric powertrain.
7. Regenerative Braking System
Electric cars often incorporate regenerative braking technology, which enables the recovery of kinetic energy during deceleration or braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the motor acts as a generator, converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then fed back to the battery, increasing efficiency and extending the vehicle’s driving range.
8. Thermal Management System
The thermal management system regulates the temperature of various powertrain components, including the battery pack and motor. It ensures optimal operating conditions, preventing overheating and maintaining performance and longevity. Efficient cooling and heating mechanisms play a vital role in maximizing powertrain efficiency and reliability.
9. Auxiliary Systems
Electric car powertrains encompass several auxiliary systems that support overall vehicle operation. These include the power steering system, air conditioning, and heating systems, as well as other electrical components such as lights, infotainment systems, and safety features. These systems draw power from the battery pack and contribute to the overall functionality and comfort of the electric vehicle.
Understanding the components of an electric car powertrain unravels the intricacies of its operation. The electric motor, battery pack, power inverter, battery management system, motor controller, transmission, regenerative braking system, thermal management system, and auxiliary systems work synergistically to provide efficient, environmentally friendly, and enjoyable transportation. As the electric vehicle industry continues to evolve, advancements in powertrain technologies will further enhance performance, range, and sustainability.
FAQ for Components of Powertrain of Electric Car
1. What is a powertrain?
A powertrain is a system that transfers power from the engine or motor to the wheels of a vehicle. In an electric car, the powertrain consists of several key components, including the battery pack, electric motor, controller, inverter, and charger.
2. What is the battery pack in an electric car?
The battery pack is the heart of an electric car, storing the electrical energy that powers the motor. It consists of numerous individual battery cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
3. What is the electric motor in an electric car?
The electric motor is the component that converts the stored electrical energy from the battery pack into mechanical energy that rotates the wheels of the car. Electric motors are highly efficient, converting a significant portion of the electrical energy into useful work.
4. What is the controller unit in an electric car?
The controller unit, also known as the powertrain control module (PCM), manages the flow of electricity from the battery pack to the motor and regulates the motor’s speed and torque. It monitors various sensors throughout the vehicle to optimize performance and efficiency.
5. What is the inverter in an electric car?
The inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity stored in the battery pack into alternating current (AC) electricity that is used by the motor. AC electricity is more efficiently transmitted and utilized in electric motors compared to DC electricity.
6. What is the charger in an electric car?
The charger is the device that replenishes the electrical energy in the battery pack. It converts the alternating current (AC) electricity from the grid into direct current (DC) electricity that can be stored in the battery. Charging times vary depending on the battery size, charger type, and available power supply.
7. What is the transmission in an electric car?
In some electric cars, a transmission is used to transfer mechanical power from the electric motor to the wheels. This is particularly common in electric vehicles with multiple motors or those designed for off-road or high-performance applications.
8. What is the thermal management system in an electric car?
Electric vehicles require a thermal management system to maintain proper operating temperatures for the battery pack, electric motor, and other components. This system ensures optimal performance and longevity by regulating temperature and cooling the components when needed.
9. What is the vehicle control unit (VCU) in an electric car?
The vehicle control unit serves as the “brain” of the electric car. It manages and coordinates various systems, including the electric motor, battery, charging, and regenerative braking. The VCU controls power distribution, monitors vehicle performance, and enables communication between different components.
10. What is the regenerative braking system in an electric car?
All-electric cars often feature regenerative braking, which harnesses kinetic energy during braking or deceleration. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the battery for later use, improving overall efficiency and extending the vehicle’s range.